一、树
1. 小结

2. 树的术语


3. 树的种类

4. 二叉树



5. 二叉树的存储
- 顺序存储

- 链式存储

- 完全二叉树适用于顺序存储,不完全二叉树适用于链式存储
6. 树的应用场景
- xml、html
- 路由协议
- mysql的索引(二叉搜索树)

- 文件系统目录结构
- 机器学习经典算法——决策树等
7. 二叉树的性质

8. 完全二叉树的代码实现
import queue
class BinaryTree():
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.lnode = None
self.rnode = None
class BinaryTree():
def __init__(self, node=None):
self.root = node
def add(self, item):
que = queue.Queue()
if not self.root:
self.root = item
return
que.put(self.root)
while True:
cur = que.get()
if not cur.lnode:
cur.lnode = item
return
else:
que.put(cur.lnode)
if not cur.rnode:
cur.rnode = item
return
else:
que.put(cur.rnode)
# 广度优先遍历,参考下方
def bfs(self):
pass
# 深度优先遍历,参考下方
def dfs(self):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = BinaryNode(1)
b = BinaryNode(2)
c = BinaryNode(3)
d = BinaryNode(4)
e = BinaryNode(5)
f = BinaryNode(6)
g = BinaryNode(7)
tree = BinaryTree()
tree.add(a)
tree.add(b)
tree.add(c)
tree.add(d)
tree.add(e)
tree.add(f)
tree.add(g)
tree.bfs()
二、树的遍历
1. 广度优先(BFS)

# 采用队列先进先出的思想,将节点依次入队
def bfs(self):
if not self.root:
return
que = queue.Queue()
que.put(self.root)
while not que.empty():
cur = que.get()
print(cur.val)
if cur.lnode:
que.put(cur.lnode)
if cur.rnode:
que.put(cur.rnode)
2. 深度优先(DFS)

1. 三种深度优先遍历

2. 代码实现
# 深度优先 —— 前序遍历
def pre_dfs(self, root):
if root:
print(root.val)
self.pre_dfs(root.lnode)
self.pre_dfs(root.rnode)
# 深度优先 —— 中序遍历
def in_dfs(self, root):
if root:
self.in_dfs(root.lnode)
print(root.val)
self.in_dfs(root.rnode)
# 深度优先 —— 后序遍历
def after_dfs(self, root):
if root:
self.after_dfs(root.lnode)
self.after_dfs(root.rnode)
print(root.val)
3. 根据遍历结果反推二叉树结构
三、树的变种
1. 红黑树
1. 定义
- 二叉查找树(BST):又叫二叉排序树,二叉搜索树,时间复杂度为O(logn),它有以下特点:

- 红黑树本质是一颗特殊的二叉查找树(自平衡的BST),它的优势是:防止BST退化成链表而导致查询效率下降到O(n);
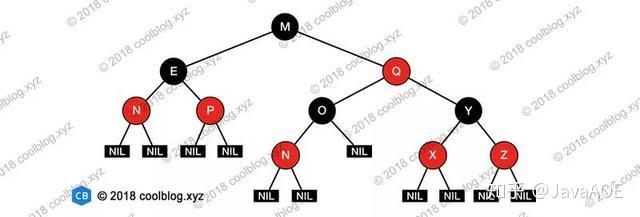
- 红黑树的性质:
- 1.每个节点或是红色的,或是黑色的。
- 2.根节点是黑色的。
- 3.每个叶节点(NIL)是黑色的。
- 4.如果一个节点是红色的,则它的俩个字节点都是黑色的。
- 5.对每个节点,从该节点到其他所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点。
2. 图示
3. 构建红黑树
todo
4. 如何处理冲突
插入节点后,为了满足红黑树的性质,使用以下规则处理冲突(即不满足红黑树规则的地方):
- 变颜色:红变黑,黑变红
- 左旋:

- 右旋:

5. 编码实现
2. B树、B+树
1. hashmap和红黑树的局限
- 为什么不使用hashmap来实现mysql的索引?
- 因为hash函数会计算一个函数值,hash(userid)=key,userid变化了,key也会变化;
- 联合索引:hash(userid+name)=key=》如果只传了userid不能支持部分索引查询以及范围查找;
- 红黑树为什么不适合mysql的索引?
- 二叉树层数太深,读取磁盘次数过多
- 磁盘1页有16K,只存单个节点数据浪费空间
2. B-tree定义
- b-tree图示
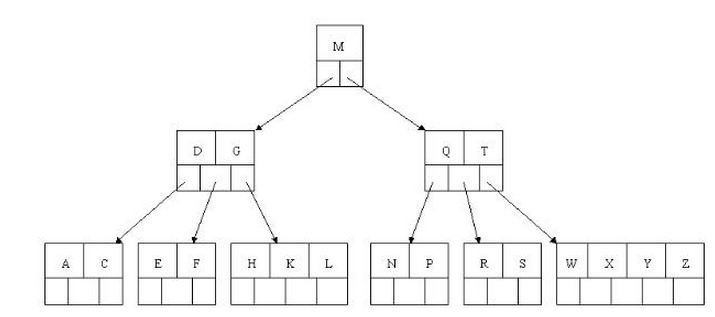
- 性质:

3. B+tree定义
- b+tree图示
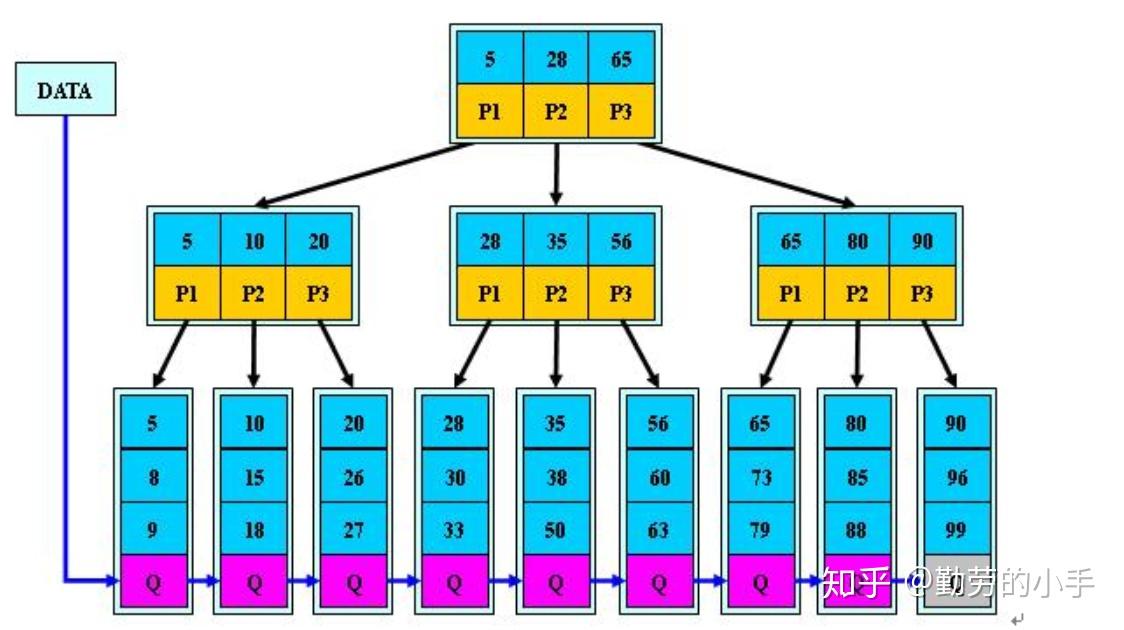
- 性质:

4. 构建B+tree
分裂,todo
5. B+tree的优点
- B+的磁盘读写代价更低
B+的内部结点并没有指向关键字具体信息的指针。因此其内部结点相对B树更小。如果把所有同一内部结点的关键字存放在同一盘块中,那么盘块所能容纳的关键字数量也越多。一次性读入内存中的需要查找的关键字也就越多。相对来说IO读写次数也就降低了。
- B+tree的查询效率更加稳定
由于非终结点并不是最终指向文件内容的结点,而只是叶子结点中关键字的索引。所以任何关键字的查找必须走一条从根结点到叶子结点的路。所有关键字查询的路径长度相同,导致每一个数据的查询效率相当。
3. 哈夫曼树
1. 定义
- 当用 n 个结点(都做叶子结点且都有各自的权值)试图构建一棵树时,如果构建的这棵树的带权路径长度最小,称这棵树为“最优二叉树”,有时也叫“赫夫曼树”或者“哈夫曼树”。
- 相关概念:

2. 图示

3. 应用
- 哈夫曼编码: 哈夫曼树的应用很广,哈夫曼编码就是其在电讯通信中的应用之一。广泛地用于数据文件压缩的十分有效的编码方法。其压缩率通常在20%~90%之间。